03. 单链表
单链表:连接数据的链条
单链表是一种基本的数据结构,通过节点之间的引用关系,将数据连接成链条。
1. 单链表的基本概念
单链表由节点组成,每个节点包含两部分:数据和指向下一个节点的引用。节点之间的链接形成了一个链表,最后一个节点的引用为空,表示链表的结束。
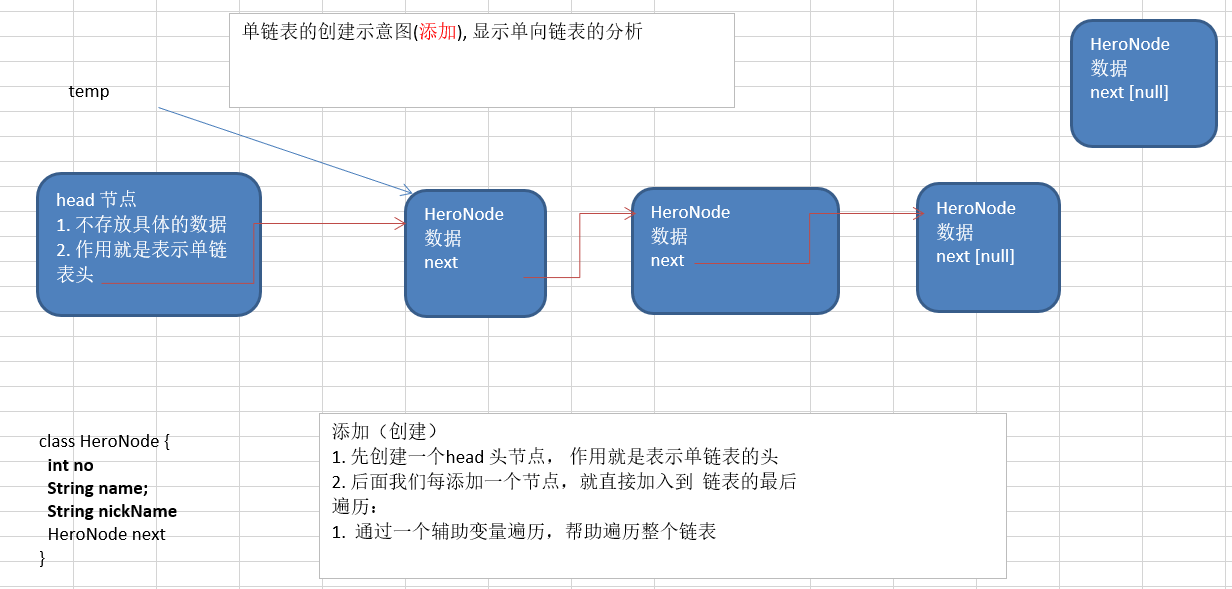
2. 单链表的实现
2.1 Java实现单链表的基本操作
package org.example;
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode heroNode1 = new HeroNode(1, "一号", "1号");
HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2, "二号", "2号");
HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3, "三号", "3号");
HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4, "四号", "4号");
HeroNode heroNode5 = new HeroNode(4, "四号", "4号");
HeroNode heroNode6 = new HeroNode(6, "六号", "6号");
// 创建链表
SinglelinkedList singlelinkedList = new SinglelinkedList();
// 加入
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode1);
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode2);
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode3);
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode4);
singlelinkedList.list();
singlelinkedList.del(heroNode3);
singlelinkedList.list();
// singlelinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode5);
// singlelinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode6);
// singlelinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode3);
// singlelinkedList.list();
}
}
//定义SingleLinkedList来管理角色
class SinglelinkedList {
// 初始化头节点,不动头节点
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 添加节点搭配单向链表
// 思路:不考虑编号顺序时,
// 找到当前链表的最后节点,并将其next指向新的节点
HeroNode temp = head;
// 遍历链表,找到最后一个
while (true) {//退出循环时,temp指向最后
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = heroNode;
}
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode temp = head;
// temp位于添加的前一个节点
boolean flag = false;//添加的编号是否存在
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {//处在链表最后
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {//位置找到了
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
flag = true;//说明编号存在
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
// 判断flag
if (flag) {
System.out.println("准备插入的编号已经存在,不能加入");
} else {
//添加到链表中
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
// 根据no修改节点的信息
public void update(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 判断是否为空
if (heroNode.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//找到需要修改的节点,根据no修改.遍历
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.no == heroNode.no) {
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag) {
temp.nickname = heroNode.nickname;
temp.name = heroNode.name;
} else {
System.out.println("未找到编号");
}
}
public void del(HeroNode heroNode) {
// 判断是否为空
if (heroNode.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else {
System.out.println("要删除的不存在");
}
}
// 显示链表
public void list() {
// 先判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
// 因为头节点不能动,因此需要辅助变量进行遍历
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
return;
}
// 输出节点信息|
System.out.println(temp);
// temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
//定义HeroNode,每个HeroNode对象就是一个节点
class HeroNode {
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next;
// 构造器
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.name = name;
this.no = no;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2.2 Python实现单链表的基本操作
# 定义 HeroNode 类,每个 HeroNode 对象就是一个节点
class HeroNode:
def __init__(self, no, name, nickname):
self.no = no
self.name = name
self.nickname = nickname
self.next = None
def __str__(self):
return f"HeroNode{{no={self.no}, name='{self.name}', nickname='{self.nickname}'}}"
# 定义 SingleLinkedList 类来管理角色
class SingleLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
# 初始化头节点,不动头节点
self.head = HeroNode(0, "", "")
def add(self, hero_node):
# 添加节点搭配单向链表
# 思路:不考虑编号顺序时,
# 找到当前链表的最后节点,并将其 next 指向新的节点
temp = self.head
# 遍历链表,找到最后一个
while temp.next is not None:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = hero_node
def add_by_order(self, hero_node):
temp = self.head
# temp 位于添加的前一个节点
flag = False # 添加的编号是否存在
while temp.next is not None:
if temp.next.no > hero_node.no: # 位置找到了
break
elif temp.next.no == hero_node.no:
flag = True # 说明编号存在
break
temp = temp.next
# 判断 flag
if flag:
print("准备插入的编号已经存在,不能加入")
else:
# 添加到链表中
hero_node.next = temp.next
temp.next = hero_node
def update(self, hero_node):
# 判断是否为空
if self.head.next is None:
print("链表为空")
return
# 找到需要修改的节点,根据 no 修改。遍历
temp = self.head.next
flag = False
while temp.next is not None:
if temp.no == hero_node.no:
flag = True
break
temp = temp.next
if flag:
temp.nickname = hero_node.nickname
temp.name = hero_node.name
else:
print("未找到编号")
def delete(self, hero_node):
# 判断是否为空
if self.head.next is None:
print("链表为空")
return
temp = self.head
flag = False
while temp.next is not None:
if temp.next.no == hero_node.no:
flag = True
break
temp = temp.next
if flag:
temp.next = temp.next.next
else:
print("要删除的不存在")
def display(self):
# 先判断链表是否为空
if self.head.next is None:
print("链表为空")
return
# 因为头节点不能动,因此需要辅助变量进行遍历
temp = self.head.next
while temp is not None:
# 输出节点信息
print(temp, end=" -> ")
# temp 后移
temp = temp.next
print("None")
if __name__ == "__main__":
hero_node1 = HeroNode(1, "一号", "1号")
hero_node2 = HeroNode(2, "二号", "2号")
hero_node3 = HeroNode(3, "三号", "3号")
hero_node4 = HeroNode(4, "四号", "4号")
hero_node5 = HeroNode(4, "四号", "4号")
hero_node6 = HeroNode(6, "六号", "6号")
# 创建链表
single_linked_list = SingleLinkedList()
# 加入
single_linked_list.add(hero_node1)
single_linked_list.add(hero_node2)
single_linked_list.add(hero_node3)
single_linked_list.add(hero_node4)
single_linked_list.display()
single_linked_list.delete(hero_node3)
single_linked_list.display()
# single_linked_list.add_by_order(hero_node5)
# single_linked_list.add_by_order(hero_node6)
# single_linked_list.add_by_order(hero_node3)
# single_linked_list.display()
3. 单链表的优势
3.1 动态插入和删除
相比于数组,单链表支持高效的动态插入和删除操作。只需调整节点的引用,而不需要移动大量元素。
3.2 空间灵活利用
单链表在空间利用上更为灵活,可以动态分配内存空间,避免了固定大小的数组的限制。
4. 单链表的应用场景
4.1 数据存储
单链表常用于需要频繁插入和删除数据的场景,如数据库系统的索引结构。
4.2 链表队列
在队列的实现中,单链表可以作为底层数据结构,实现高效的入队和出队操作。
5. 总结
单链表作为一种基础而灵活的数据结构,在计算机科学中扮演着重要角色。通过节点之间的引用关系,它提供了一种动态、高效的数据组织方式,特别适用于需要频繁插入和删除操作的场景。通过深入理解单链表的基本概念和实现方式。在解决实际问题时,单链表是一个强大而灵活的工具,为数据的有序存储和操作提供了可靠的基础。